2024 / 04 / 17
Nitrous Oxide: Beyond the Laughing Gas
Nitrous oxide, also known as “laughing gas,” is a colorless and odorless gas with a sweet taste. While it is commonly used as a sedative in dental procedures and childbirth, nitrous oxide has also gained popularity for its recreational use in recent years. However, its effects go beyond just inducing laughter and euphoria. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which nitrous oxide has been used and depicted in literature, music, film, counterculture movements, and society, as well as its health risks and environmental consequences.

Nitrous Oxide in Literature and Music: From Hunter S. Thompson to the Grateful Dead
Nitrous oxide has been a recurring theme in literature and music, particularly in counterculture movements.
In Hunter S. Thompson‘s novel Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas, the protagonist uses nitrous oxide to enhance his psychedelic experiences.

The Grateful Dead, a legendary rock band from the 1960s, incorporated nitrous oxide into their live performances, with fans often inhaling it from balloons passed around the audience.
Other artists who have referenced nitrous oxide in their work include rapper Lil Wayne, who has mentioned using it in his songs, and electronic musician Aphex Twin, who included the sound of nitrous oxide being inhaled in one of his tracks.
The use of nitrous oxide in these works of art not only reflects its popularity in certain subcultures but also highlights its potential for creative inspiration and sensory exploration.
Nitrous Oxide in Film and TV: Escapism and Coping Mechanisms
Nitrous oxide has also been featured in films and television shows, often as a tool for escapism or a coping mechanism.
In the TV series Breaking Bad, the character Jesse Pinkman inhales nitrous oxide to deal with the stress of his criminal activities.
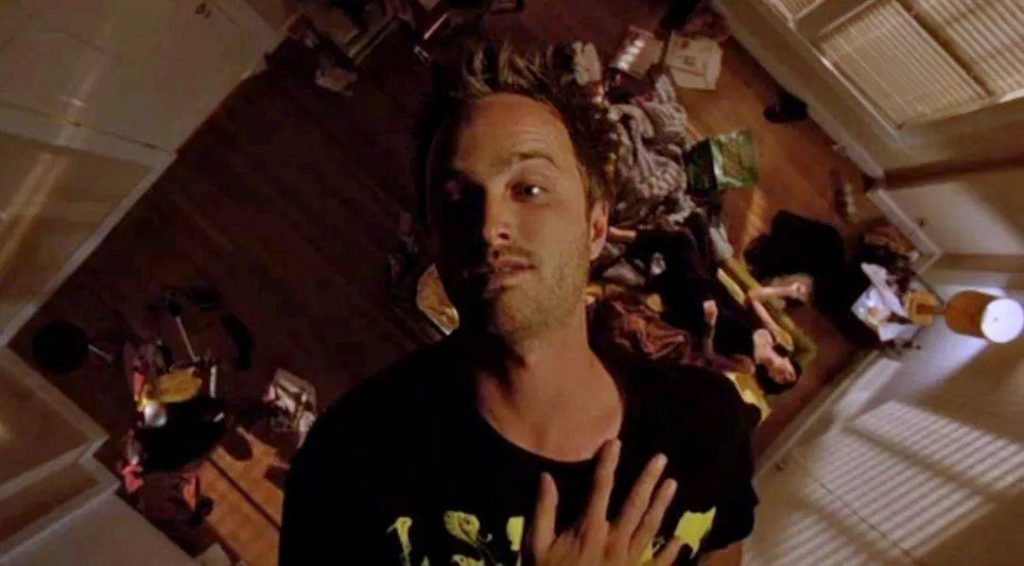

Breking Bad Jesse
In the film The Beach, the protagonist uses nitrous oxide to escape the monotony of everyday life.
These portrayals of nitrous oxide in media raise questions about the social and psychological factors that drive people to use it and the potential consequences of such use.
Nitrous Oxide in Counterculture Movements: Spiritual Enlightenment and Liberation
Nitrous oxide has played a significant role in counterculture movements throughout history, from the Beat Generation of the 1950s to the rave scene of the 1990s.
In these subcultures, nitrous oxide has been associated with spiritual enlightenment, liberation, and transcendence. Some argue that the gas can induce mystical experiences or even facilitate contact with higher consciousness. However, others caution that the risks associated with nitrous oxide use can outweigh any potential benefits. In addition, the use of nitrous oxide in these contexts often raises questions of cultural appropriation, as certain rituals and practices involving nitrous oxide have their roots in indigenous cultures.
Nitrous Oxide in Society: Legal and Ethical Implications
Despite its widespread use, nitrous oxide is not without legal and ethical considerations. In many countries, nitrous oxide is classified as a controlled substance and is illegal to possess or distribute for recreational purposes.
The UK, for example, has recently tightened its regulations on nitrous oxide, making it illegal to supply or import the gas for human consumption.

An article in the British Medical Journal last year noted the need for increased awareness of the potential dangers of nitrous oxide abuse due to what it called an “epidemic” of use among young people while at festivals, nightclubs and parties.
Doctors raised concerns over the use of the drug after more users began presenting with “neurological complications” after inhaling from large canisters of the gas from containers “80 times the size of whippits”.
“The message is clear: the laughing gas epidemic is no laughing matter at all,” wrote Tom Rawstorne in the Daily Mail. Rawstorne interviewed a receptionist from London who, the paper claimed, is in a wheelchair as a result of spinal damage caused by nitrous oxide. She told him that for “two years my body was breaking down because of all the balloons I did”. She said she no longer rememebered how it felt “not to have pain”, and that the gas was “way more dangerous than people think”.
——– THE WEEK, UK.
Additionally, the environmental impact of nitrous oxide cannot be ignored, as it is a potent greenhouse gas and contributes to global warming. The production, transportation, and disposal of nitrous oxide can also have negative impacts on the environment.
Nitrous Oxide Use: Health Risks and Environmental Consequences
While nitrous oxide is generally considered safe when used in medical settings, recreational use carries various health risks. Inhaling nitrous oxide can cause recreational use and carries various health risks.
Inhaling nitrous oxide can cause dizziness, confusion, and loss of coordination, which can lead to falls and injuries.
It can also cause oxygen deprivation and result in long-term neurological damage.
Chronic use can lead to vitamin B12 deficiency, which can cause nerve damage and other serious health problems.
Moreover, the production and consumption of nitrous oxide have environmental consequences. Nitrous oxide is a potent greenhouse gas that is over 300 times more potent than carbon dioxide, and its release into the atmosphere contributes to climate change.
Conclusion: A Balanced View of Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous oxide has gained popularity for its recreational use in recent years, but its effects and consequences go beyond inducing laughter and euphoria.
While nitrous oxide has been depicted in literature, music, film, and counterculture movements as a tool for creativity, spiritual enlightenment, and liberation, its use also raises legal, ethical, health, and environmental concerns.
A balanced view of nitrous oxide acknowledges its potential benefits as well as its risks and consequences and promotes responsible use and regulation.










